CIFFA Exam Sample Practice Questions & Answers – Transportation Geography

CIFFA Exam Sample Practice Questions & Answers – Transportation Geography
Questions
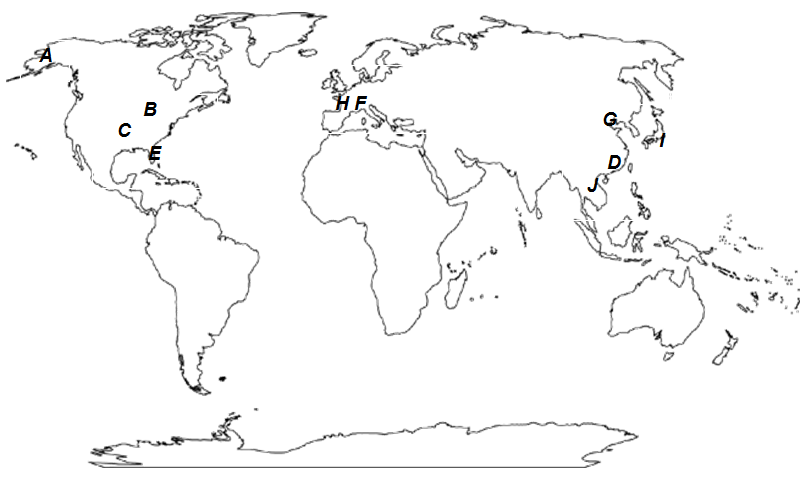
- On the map below, indicate the top 10 key gateway cargo airports, beside each letter.
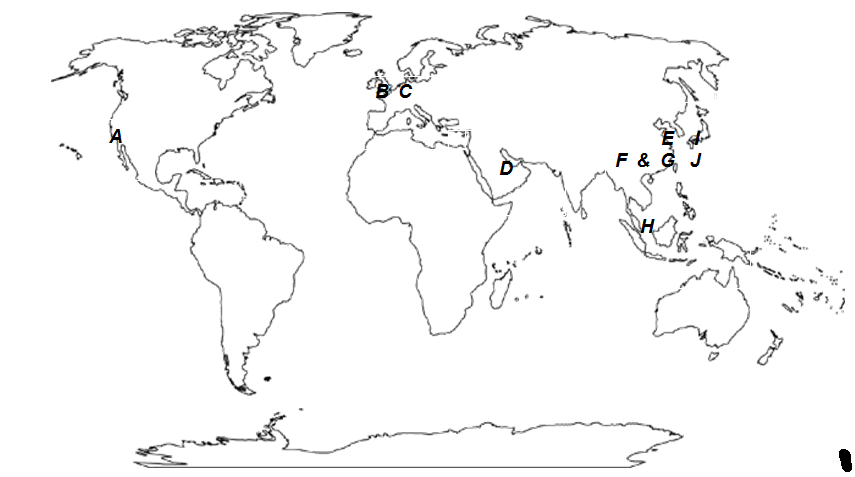
- On the map below, indicate the top 10 key gateway seaports, beside each letter.
- Name 5 major container ports from where known scheduled inland barge services operate (via river or canal) including the inland destinations or regions served.
- Name 5 major container ports which are well known as “transshipment hubs” and explain some key regions of the feeder destinations.
- Name 3 major transshipment hubs in:
a) North America
b) Europe
c) Asia
- If you wanted to ship with the same airline cargo from Chicago, USA to Frankfurt, Germany, which routing (i.e., transshipment airports) can you expect from the following national carriers of these countries:
a) USA
b) France
c) UK
d) Germany
e) Denmark
- Sea/air combination traffic is offered by several airlines as an alternative to all ocean or all water transportation between the Far East and Europe. Which airports are known as transshipment points in those trade lanes?
- How did containerization affect world transportation geography?
- List the five modes of transportation.
- Name 3 trade agreements.
- Name 3 major ocean canals.
- Name 3 ocean navigable rivers around the world.
- List the key gateway container seaports in South America.
- List the major airports in South America.
- List the land-locked countries in South America.
- List the capitals for each of the following: Norway, Finland, Sweden, Denmark, United Kingdom, Ireland, Germany, Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Monaco, Austria, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Slovenia, Albania, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Macedonia, Greece, Turkey.
- Identify the landlocked countries in Europe and how sea access is gained.
- List the key gateway container seaports in Northern Europe, and the Mediterranean.
- List the key gateway cargo airports in Northern Europe, and the Mediterranean.
- List the other major airports in Northern Europe, and the Mediterranean.
- List the key gateway container seaports in the Middle East.
- List the major airports in the Middle East.
- How does Iraq gain access to the Persian Gulf?
- Identify the two countries that are connected by a major causeway.
- Identify the capitals of five North African countries.
- Identify key feeder ports in Africa.
- List the major South African seaports and airports.
- List the capitals of the following countries in Central Asia: Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
- Which two inland seas border these countries?
- What countries can conceivably be used for access to sea routes?
- List the capitals of the following countries in East Asia: China, Mongolia, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan.
- List the key gateway container seaports in East Asia.
- List the key gateway cargo airports in East Asia.
- List the capitals of the following countries in the Indian Sub-continent: India, Pakistan and Bangladesh
- List the key gateway container seaports in this region.
- List the other major ports and major airports for each of the three major countries.
- List the capitals of the following countries in Southeast Asia: Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei, Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Singapore.
- List the key gateway container seaports in this region.
- List the major airports in this region.
- List the capitals of Australia and New Zealand (South Pacific).
- List the key gateway container seaports in the South Pacific.
- List the major airports in the South Pacific.
- Define the meaning of the expression “Oceania.”
- Identify the three main island groups comprising Oceania.
Calculating Current Time
Assume all countries are on “Standard Time.”
- What is the time in Vancouver (GMT – 8) if it is 21:30 on Tuesday in Halifax (GMT – 4)?
- What time is it in Amsterdam (GMT + 1) if it is 07:00 on Monday in Montreal (GMT – 5)?
- What time is it in Tokyo (GMT + 9) if it is 16:30 on Friday in Toronto (GMT – 5)?
- What time is it in Sydney (GMT + 10) if it is 13:00 on Wednesday in Honolulu (GMT – 10)?
- What time is it in St. John’s (GMT – 3 1/2) if it is 10:00 on Saturday in Los Angeles (GMT – 8)?
- What time is it in London (GMT 0) if it is 00:30 on Thursday in Paris (GMT +1)?
- What time is it in Johannesburg (GMT + 2) if it is 11:30 on Monday in New York (GMT – 5)?
Calculating Shipment’s Arrival Time
Assume all countries are on “Standard Time.”
- What time does the shipment arrive in San Francisco (GMT – 8), if it departs Calgary (GMT – 7) at 13:30 on Monday? Air Canada has a 2 ½ hour flight.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Dallas (GMT – 6), if it departs Edmonton (GMT – 7) at 12:45 on Thursday? United Airlines has a 3 hour 15 minute flight.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Houston (GMT – 6), if it departs Montreal (GMT – 5) at 08:00 Wednesday? Atlantis Transportation has a truck leaving Montreal for Toronto that takes 8 hours. There is a 2 hour 45 minute connection time in Toronto. Air Canada has a 3 hour 30 minute flight to Houston.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Moscow (GMT + 3), if it departs London (GMT 0) at 08:40 on Monday? British Airways has a 4 hour flight.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Paris (GMT + 1), if it departs New York (GMT – 5) at 22:00 on Wednesday? American Airlines 7 ½ hour flight.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Sydney (GMT + 10), if it departs Vancouver (GMT – 8) at 00:45 on Friday? Air Canada has a 15 hour flight.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Buenos Aires (GMT – 4), if it departs Toronto (GMT – 5) at 17:30 on Tuesday? Continental Airlines has a 3 ½ hour flight to Houston, a 2 hour connection, then a 10 ½ hour flight to Buenos Aires.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Halifax (GMT – 4), if it departs Beijing (GMT + 8) at 17:30 on Saturday? United Airlines has a 13 hour flight to Chicago, a 2 hour 30 minute connection, then a 3 hour flight to Halifax.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Montreal (GMT – 5), if it departs Shanghai (GMT + 8) at 13:00 on Wednesday, October 1? OOCL’s ship transits to Vancouver in 15 days (360 hours). There is a 54 hour connection time (off-loading and transfer to rail yard). CP Rail transits to Montreal in 5 days (120 hours). There is a 36 hour delivery time to the forwarders warehouse in Montreal (including pick-up time at the rail yard).
Answers
- On the map below, indicate the top 10 key gateway cargo airports, beside each letter.
A Anchorage
B Louisville
C Memphis
D Shanghai (Pudong)
E Miami
F Frankfurt
G Seoul (Incheon)
H Paris (Charles de Gaulle)
I Tokyo (Narita)
J Hong Kong
- On the map below, indicate the top 10 key gateway seaports, beside each letter.
A Los Angeles
B Rotterdam
C Hamburg
D Dubai
E Shanghai
F Hong Kong or Shenzhen
G Shenzhen or Hong Kong
H Singapore
I Pusan (Busan)
J Kaohsiung
- Name 5 major container ports from where known scheduled inland barge services operate (via river or canal) including the inland destinations or regions served.
Antwerp, Rotterdam (inland Germany, France, Switzerland via the Rhine River).
Hamburg (via the Elbe into German hinterland).
Marseille (via the Rhone to Lyon, France).
Shanghai (via the Yangtze into China’s interior).
Buenos Aires (via the Plate/Parana to Paraguay).
- Name 5 major container ports which are well known as “transshipment hubs” and explain some key regions of the feeder destinations.
Antwerp, Rotterdam, Hamburg (for UK, Baltics and Norwegian ports).
Marseille (France), Malta (Malta), Piraeus (Greece) for Mediterranean and Black Sea destinations.
Dubai (UAE) for Gulf/Middle East ports.
Singapore for South East Asia region.
Freeport, Bahamas (for Caribbean Sea).
Manzanillo (Panama) for Far East/South America/North America.
- Name 3 major transshipment hubs in:
a) North America
New York, Chicago, Miami, Los Angeles, Seattle, Minneapolis, Denver, Houston.
b) Europe
London, Amsterdam, Frankfurt, Paris.
c) Asia
Singapore, Tokyo, Seoul, Taipei, Hong Kong.
- If you wanted to ship with the same airline cargo from Chicago, USA to Frankfurt, Germany, which routing (i.e. transshipment airports) can you expect from the following national carriers of these countries:
a) USA: Minneapolis, Detroit, Atlanta, New York.
b) France: Paris.
c) UK: London.
d) Germany: Frankfurt – direct.
e) Denmark: Copenhagen.
- Sea/air combination traffic is offered by several airlines as an alternative to all ocean or all water transportation between the Far East and Europe. Which airports are known as transshipment points in those trade lanes?
Vancouver, BC; Seattle, Oakland/Los Angeles.
- How did containerization affect world transportation geography?
The “door-to-door” concept became a new norm, containers could be moved overland by truck or rail and then be loaded onto a ship without ever transloading.
- List the five modes of transportation.
Rail, road, air, water and pipeline.
- Name 3 trade agreements.
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (1948), the Benelux Economic Union (1948), the European Economic Community (Common Market, 1957), the European Free Trade Association (1959), Mercosur (the Southern Cone Common Market, 1991), and the World Trade Organization (1995). In 1993, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
- Name 3 major ocean canals.
Panama, Suez and Kiel.
- Name 3 ocean navigable rivers around the world.
Great Lakes/St. Lawrence Seaway and River System, Columbia River, Amazon River and the River Plate.
- List the key gateway container seaports in South America.
Santos, Brazil.
- List the major airports in South America.
Bogotá, Columbia
Caracas, Venezuela
Georgetown, Guyana
Paramaribo, Suriname
Cayenne, French Guiana
Brasilia, Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Puorto Alegre, Brazil
Quito, Ecuador
Lima, Peru
La Paz, Sucre, Bolivia
Santiago, Chile
Asuncion, Paraguay
Buenos Aires, Argentina
Montevideo, Uruguay.
- List the land-locked countries in South America.
Bolivia and Paraguay.
- List the capitals of the following countries.
Scandinavia:
Oslo, Norway
Helsinki, Finland
Stockholm, Sweden
Copenhagen, Denmark.
UK/Ireland:
London, United Kingdom
Dublin, Ireland.
Western Europe:
Berlin, Germany
Amsterdam, Netherlands
Brussels, Belgium
Luxembourg, Luxembourg
Paris, France
Monaco, Monaco
Vienna, Austria
Bern, Switzerland
Rome, Italy
Madrid, Spain
Lisbon, Portugal.
Russia and former dependencies:
Moscow, Russia
Tallinn, Estonia
Riga, Latvia
Vilnius, Lithuania
Minsk, Belarus
Kiev, Ukraine Kishinev, Moldova
Tbilisi, Georgia
Yerevan, Armenia
Baku, Azerbaijan.
Central and Eastern Europe:
Warsaw, Poland
Prague, Czech Republic
Bratislava, Slovakia
Budapest, Hungary
Bucharest, Romania
Sofia, Bulgaria.
Balkans:
Ljubljana, Slovenia
Tirana, Albania
Zagreb, Croatia
Belgrade, Serbia
Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina
Skopje, Macedonia
Athens, Greece
Ankara, Turkey.
- Identify the landlocked countries in Europe and how sea access is gained.
Luxembourg – excellent road and rail access to various ports in Belgium and the Netherlands.
Austria – excellent road and rail access to all major ports in Europe as it is centrally located.
Switzerland – excellent road and rail access to all major ports in Europe as well as its own merchant marine fleet in the ports of Marseilles, France and Genoa, Italy.
Belarus – access to sea through Lithuania and Latvia.
Moldova – access to Odessa and some Russian ports on the Black sea.
Armenia – port access through Georgia and Turkey.
Czech Republic – sea access by rail and road to ports of Hamburg, Bremen, Rostock, Rotterdam, Antwerp, Gdansk and others.
Slovakia – same as Czech Republic above.
Hungary – same as Czech Republic above.
Bosnia-Herzegovina – access through ports in Croatia.
Macedonia – sea access through ports in Greece and Albania.
- List the key gateway container seaports in Western and Northern Europe, and the Mediterranean.
Felixstowe, UK
Hamburg, Germany
Bremen/Bremerhaven, Germany
Rotterdam, Netherlands
Antwerp, Belgium
Le Havre, France
Gioia Tauro, Italy
Barcelona, Valencia, Algeciras Bay, Spain.
- List the key gateway cargo airports in Northern Europe, and the Mediterranean.
Frankfurt, Munich, Germany
Cologne/Bonn, Germany
Amsterdam, Netherlands
London, UK
Brussels, Belgium
Luxembourg, Luxembourg
Paris, France
Madrid, Spain.
- List the other major airports in Northern Europe, and the Mediterranean.
Oslo, Norway
Helsinki, Finland
Stockholm, Sweden
Copenhagen, Denmark
Manchester, Edinburgh, Dublin, UK/Ireland
Munich, Germany
Vienna, Austria
Zurich, Geneva, Switzerland
Rome, Italy
Barcelona, Spain
Lisbon, Portugal.
- List the key gateway container seaports in the Middle East.
Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Dubai, Khor Fakkan, UAE
Salalah, Oman.
- List the major airports in the Middle East.
Tehran, Iran
Baghdad, Iraq
Damascus, Syria
Beirut, Lebanon
Tel Aviv, Israel
Amman, Jordan
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Kuwait, Kuwait
Manama, Bahrain
Doha, Qatar
Dubai, UAE
Muscat, Oman
Sanaa, Yemen.
- How does Iraq gain access to the Persian Gulf?
Through its principal seaports of Umm Qasr and Basra, as well as the ports of Beirut, Lebanon and Lattakia, Syria.
- Identify the two countries that are connected by a major causeway.
Bahrain and Saudi Arabia are connected by the King Fahd causeway.
- Identify the capitals of five North African countries.
Tunis, Tunisia
Algiers, Algeria
Rabat, Morocco
Tripoli, Libya
Cairo, Egypt.
Answers Transportation Geography
Page | 33
2017
- Identify key feeder ports in Africa.
Durban, Cape Town, Port Elizabeth, South Africa
Casablanca, Morocco
Tunis, Tunisia
Djibouti, Djibouti
Maputo, Mozambique
Lagos, Nigeria.
- List the major South African seaports and airports.
Ports:
Durban
Cape Town
Port Elizabeth
East London.
Airports:
Johannesburg
Cape Town
Durban.
- List the capitals of the following countries in Central Asia.
Kabul, Afghanistan
Astana, Kazakhstan
Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan
Dushanbe, Tajikistan
Ashkhabab, Turkmenistan
Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
- Which two inland seas border these countries?
Caspian and Aral Sea.
- What countries can conceivably be used for access to sea routes?
Russia, Pakistan, and Iran.
- List the capitals of the following countries in East Asia.
Beijing, China
Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
Rangoon, Myanmar
Bangkok, Thailand
Vientiane, Laos
Phnom-Penh, Kampuchea (Cambodia)
Hanoi, Vietnam
Pyongyang, North Korea
Seoul, South Korea
Taipei, Taiwan
Tokyo, Japan.
- List the key gateway container seaports in East Asia.
Hong Kong, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Qingdao, Ningbo, Tianjin, Guangzhou Harbour/Huangpu, Xiamen, Dalian, China
Pusan, South Korea
Kaohsiung, Keelung, Taiwan
Tokyo, Yokohama, Nagoya, Osaka, Kobe, Japan
Laem Chabang, Thailand.
- List the key gateway cargo airports in East Asia.
Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, China
Seoul, South Korea
Taipei, Taiwan
Tokyo, Osaka, Japan
Bangkok, Thailand.
- List the capitals of the following countries in the Indian Sub-continent.
New Delhi, India
Islamabad, Pakistan
Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- List the key gateway container seaports in this region.
Jawaharlal Nehru, India
Colombo, Sri Lanka.
- List the other major ports and major airports for each of the three major countries.
Ports:
Mumbai, Calcutta, Chennai, India
Karachi, Port Qasim, Pakistan
Chittagong, Chalna, Bangladesh.
Airports:
New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, India
Karachi, Lahore, Islamabad, Pakistan
Dhaka, Chittagong, Bangladesh.
- List the capitals of the following countries in Southeast Asia.
Jakarta, Indonesia
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei
Manila, Philippines
Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea
Singapore, Singapore.
- List the key gateway container seaports in this region.
Tanjung Priok (Jakarta), Indonesia
Port Kelang, Tanjung Pelepas, Malaysia
Manila, Philippines
Singapore, Singapore.
List the major airports in this region.
Jakarta, Indonesia
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Brunei, Brunei
Manila, Philippines
Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea
Singapore Changi, Singapore.
- List the capitals of Australia and New Zealand (South Pacific).
Canberra, Australia
Wellington, New Zealand.
- List the key gateway container seaports in the South Pacific.
Melbourne, Australia.
- List the major airports in the South Pacific.
Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Australia
Wellington, Auckland, New Zealand.
- Define the meaning of the expression “Oceania.”
It’s a collective name for more than 10,000 islands scattered throughout most of the Pacific Ocean.
- Identify the three main island groups comprising Oceania.
Micronesia, Polynesia, Melanesia.
Calculating Current Time
Assume all countries are on “Standard Time.”
- What is the time in Vancouver (GMT – 8) if it is 21:30 on Tuesday in Halifax (GMT – 4)?
The difference is 4 hours, going west, you subtract.
21:30 – 4 hours = 17:30
The time in Vancouver would be 17:30 on Tuesday.
- What time is it in Amsterdam (GMT + 1) if it is 07:00 on Monday in Montreal (GMT – 5)?
The difference is 6 hours, going east, you add.
07:00 + 6 hours = 13:00
The time in Amsterdam would be 13:00 on Monday.
- What time is it in Tokyo (GMT + 9) if it is 16:30 on Friday in Toronto (GMT – 5)?
The difference is 14 hours, since you cannot cross the International Date Line, when going east, you add.
16:30 + 14 hours = 06:30
The time in Tokyo would be 06:30 on Saturday.
- What time is it in Sydney (GMT + 10) if it is 13:00 on Wednesday in Honolulu (GMT – 10)?
The difference is 20 hours, since you cannot cross the International Date Line, when going east, you add.
13:00 + 20 hours = 09:00
The time in Sydney would be 09:00 on Thursday.
- What time is it in St. John’s (GMT – 3 1/2) if it is 10:00 on Saturday in Los Angeles (GMT – 8)?
The difference is 4 1/2 hours, going east, you add.
10:00 + 4 1/2 hours = 14:30
The time in St. John’s would be 14:30 on Saturday.
- What time is it in London (GMT 0) if it is 00:30 on Thursday in Paris (GMT + 1)?
The difference is 1 hour, going west, you subtract.
00:30 – 1 hour = 23:30
The time in London would be 23:30 on Wednesday.
- What time is it in Johannesburg (GMT + 2) if it is 11:30 on Monday in New York (GMT – 5)?
The difference is 7 hours, going east, you add.
11:30 + 7 hours = 18:30
The time in Johannesburg would be 18:30 on Monday.
Calculating Shipment’s Arrival Time
Assume all countries are on “Standard Time.”
- What time does the shipment arrive in San Francisco (GMT – 8), if it departs Calgary (GMT – 7) at 13:30 on Monday? Air Canada has a 2 ½ hour flight.
The difference in time is 1 hour, going west you subtract 1 hour. 13:30 – 1 hour = 12:30 Add the 2 ½ flight time = 15:00 Therefore the shipment arrives in San Francisco at 15:00L on Monday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Dallas (GMT – 6), if it departs Edmonton (GMT – 7) at 12:45 on Thursday? United Airlines has a 3 hour 15 minute flight.
The difference in time is 1 hour, going east you add 1 hour. 12:45 + 1 hour = 13:45 Add the 3 hour 15 minute flight time = 17:00 Therefore the shipment arrives in Dallas at 17:00L on Thursday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Houston (GMT – 6), if it departs Montreal (GMT – 5) at 08:00 Wednesday? Atlantis Transportation has a truck leaving Montreal for Toronto that takes 8 hours. There is a 2 hour 45 minute connection time in Toronto. Air Canada has a 3 hour 30 minute flight to Houston.
The difference in time is 1 hour, going west you subtract 1 hour. 08:00 – 1 hour = 07:00 Add the 8 hour trucking time = 15:00 Add the 2 hour 45 minute connection time in Toronto = 17:45 Add the 3 hour 30 minute flight = 21:15 Therefore the shipment arrives in Houston at 21:15L on Wednesday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Moscow (GMT + 3), if it departs London (GMT 0) at 08:40 on Monday? British Airways has a 4 hour flight.
The difference in time is 3 hours, going east you add 3 hours. 08:40 + 3 hours = 11:40 Add the 4 hour flight time = 15:40 Therefore the shipment arrives in Moscow at 15:40L on Monday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Paris (GMT + 1), if it departs New York (GMT – 5) at 22:00 on Wednesday? American Airlines 7 ½ hour flight.
The difference in time is 6 hours, going east you add 6 hours. 22:00 + 6 hours = 04:00 Add the 7 ½ hour flight time = 11:30 Therefore the shipment arrives in Paris at 11:30L on Thursday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Sydney (GMT + 10), if it departs Vancouver (GMT – 8) at 00:45 on Friday? Air Canada has a 15 hour flight.
The difference is 18 hours, since you cannot cross the International Date Line, when going east, you add. 00:45 + 18 hours = 18:45 Add the 15 hour flight time = 09:45 Therefore the shipment arrives in Sydney at 09:45L on Saturday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Buenos Aires (GMT – 4), if it departs Toronto (GMT – 5) at 17:30 on Tuesday? Continental Airlines has a 3 ½ hour flight to Houston, a 2 hour connection, then a 10 ½ hour flight to Buenos Aires.
The difference in time is 1 hour, going east you add 1 hour. 17:30 + 1 hour = 18:30 Add the 3 ½ hour flight time = 22:00 Add the 2 hour connection time = 24:00 Add the 10 ½ hour flight time = 10:30L Therefore the shipment arrives in Buenos Aires at 10:30L on Wednesday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Halifax (GMT – 4), if it departs Beijing (GMT + 8) at 17:30 on Saturday? United Airlines has a 13 hour flight to Chicago, a 2 hour 30 minute connection, then a 3 hour flight to Halifax.
The difference is 12 hours, since you cannot cross the International Date Line, when going west, you subtract. 17:30 – 12 hours = 05:30 Add the 13 hour flight time = 18:30 Add the 2 hour 30 minute connection time = 21:00 Add the 3 hour flight time = 00:00L Therefore the shipment arrives in Halifax at 00:00L on Sunday.
- What time does the shipment arrive in Montreal (GMT – 5), if it departs Shanghai (GMT + 8) at 13:00 on Wednesday, October 1? OOCL’s ship transits to Vancouver in 15 days (360 hours). There is a 54 hour connection time (off-loading and transfer to rail yard). CP Rail transits to Montreal in 5 days (120 hours). There is a 36 hour delivery time to the forwarders warehouse in Montreal (including pick-up time at the rail yard).
The difference is 13 hours, since you cannot cross the International Date Line, when going west, you subtract. 13:00 – 13 hours = 00:00 Add the 360 hour transit time = 00:00 on October 16 Add the 54 hour connection time = 06:00 on October 18 Add the 120 hour transit time = 06:00 on October 23 Add the 36 hour delivery time = 18:00 on October 24 Therefore the shipment arrives in Montreal on Friday, October 24 at 18:00L.





