Global Logistics Report – Japan Freight Railway Company

Japan Freight and Logistic Overview
Japan is an island country with a scarcity of natural resources, it is surrounded by sea. As a result, it depends greatly on importing raw materials and exporting processed products. For the same reason, freight services and logistics play an important role in the economy of Japan. In 2017, this industry not only accounts for 5% of the national GDP, which is equivalent to about 25 Trillion Yen but also provides jobs for more than 2 million people across the country. Last year, Japan was ranked fifth in the best countries in logistics performance by The World Bank, improved from the 16th position in 2016 (The World Bank, 2018).
Railway is one of the key means of transportation, mainly for mass and fast transporting between big cities and major islands such as Tokyo, Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku. Due to a huge debt, most of the railway networks were privatized of which 70% is currently owned and run by Japan Railways Groups. Ever since, the privatized network has become more efficient, required fewer financial supports and operates exceptionally punctually (Warnock, 2018).
Japan Railway Groups
As mentioned above, the Japan Railways Group (JR Group) is the successor of the national Japanese National Railways. The group has a total route length of over 20,000 km, half of which is electrified. The current brand value is estimated to be more than USD 11 billion. In addition, it consists of nine railways companies of which six of them are for regional passengers, one is a research organization, one is an IT service company and one is a nationwide freight railway company- JR Freight. Together, they run a nationwide network of traditional train lines and the Shinkansen which is also known as bullet trains.
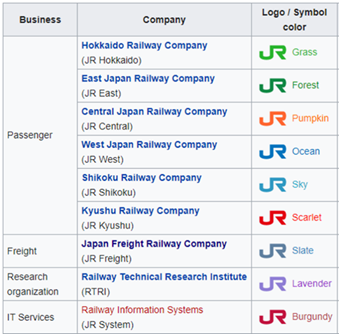
Japan Freight Railway Company
Japan Freight Railway Company, or JR Freight, is a subsidy company of JR Group that offers transportation services of cargo nationwide. The headquarter of JR Freight locates in Shibuya, Tokyo. As reported in 2018, the company owns over 550 locomotives, about 10,000 freight cars, and hires nearly 5500 employees (JR freight, 2019).
However, Japan has always been an extremely competitive market for freight. For example, the company experienced a massive loss of rail freight to other modes such as air freight, ship, and especially truck. Moreover, in the early period when JR freight was taking over the railway system from the government, there was a great impediment that the rail lines were designed based on a narrow-gauge standard which could not easily be upgraded. Consequently, the rail lines could not handle heavy trains to compete with other types of freights.
As of today, the situation has become better JR Freight for the two main factors. The first factor is that the company has continuously invested in modernizing new locomotives and fleet of container flat cars, with its most advanced trains capable of operating at over 110 kph and combine with passenger trains. For the second factor, there has been a shortage of truck drivers in Japan for the last few decades. The high-price and overloading situation of trucking services has shifted the demand for good transportation towards train freight. As a result, despite the fact that only a little more than 5 percent of all freight in Japan is carried by trains, but nearly all that operation, reportedly 99%, is done by JR Freight.
Japan Freight’s Historical Upgrades
In 2001, JR Freight had to make upgrades in order to compete with trucking companies. In order to compete with the trucking companies and increase the demand for railway shipments, they needed to upgrade freight station equipment and make changes to the services they offer more tailor-fitted to the needs of the shippers. They decided they need to run container trains at faster speeds, increase the capacity of their transports, produce a new variety of locomotives, enhance the facilities at the stations, and upgrade their information systems.
JR Freight developed lots of new high-speed container trains. They improved the efficiency of the tracks. And the government at that time made it easier for shippers to transport via rail which boosted the demand for railway transshipment. JR Freight was still using their old models but also created newer ones such as the Taki 1000 tanker wagon which had very high-performance and ran on crude oil and gasoline. This had an improved braking system making it safer to run on the tracks and can even stop a very fast container. JR Freight also developed new types of containers that were all structured differently tailor-fitted to the needs of the growing needs of shippers. Some would be able to contain frozen and cold goods to be transported to different cities in Japan. Even the stations were developed by JR Freight. They developed the Effective and Speedy Container Handling (E&S) method which allows them to load and unload directly on the tracks which make for a faster and more efficient way to transport goods since after unloading, the train could leave and move on to the next city for transport.
One of the most innovative ways JR Freight enhanced their service was by introducing two computer systems: FRENS (FREight information Network System) and NETS (NETwork of Transportation Strategy) which supported bulky shipments in tankers and hopper wagons. These systems were installed in hundreds of computers in their sales offices, stations, and freight-forwarding offices. With these, they were able to maintain a database of train reservations, track and monitor location and situations of all containers, determine the estimated time of arrival of each train, provide the contents of the containers, store and share information on the freight-forwarding companies, among other detailed information that helped them provide top-notch service.
The piggyback services provided by JR Freight in 1986 was no longer profitable in 2000 due to increasing in truck drivers, restrictions have been made on large trucks for piggyback, and the loading system was not efficient. This has led JR Freight to promote the advantages of an alternative to piggyback which was swap body transport. This meant having to carry large trucks on freight wagons (EJRCF, 2001).
Japan Freight Company’s Services
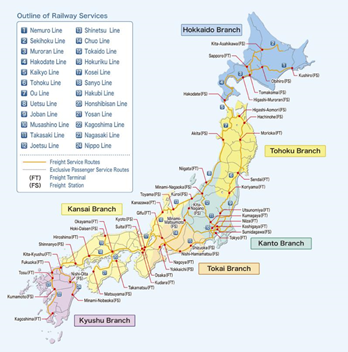
The company provides rail freight service domestically in Japan. They have several branches opened all over the country to ensure the sustainability and flexibility of the service. Currently, Japan Freight Railway Company has brought into operation a number of six branches, which are Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Tokai, Kansai, and Kyushu branch.
Japan Freight Railway Company provides not only transportation of cargo; they also offer a variety of logistics-related services. Their services include:
- Rail freight services: This is the leading service of JR Freight Company. A proportion of 99 percent of freight carried by rail in Japan is provided by JR Freight. Containers and freight cars are utilized for JR Freight’s rail service, with the ability to carry bulky and large-volume cargo, household goods, food products.
- Warehousing: Providing convenient storage space for the client’s inventory. Properly storing and handling goods with advanced technology which allow clients to efficiently keep track of their level of inventory and ensure that they have access to their goods smoothly at any point in time.
- Car park operation: Providing parking lot design and supervision on the area by taking advantages of modern parking equipment. Automated parking systems are utilized upon client’s request for the best customer experience. JR Freight offers several models to optimize the efficiency of the client’s parking space, which in turn generates profits.
- Advertising: Offer transportation and logistics advertising service. Messages of an advertisement from clients will be incorporated on vehicles of the company to increase market exposure and brand recognition.
- Indemnity and other non-life insurance agency services: Offer insurance policy that is designed to protect clients from claims of losses and damages caused by another party during transportation. The insurance will pay for a significant part of the client’s cost when filing a civil claim for their financial loss. JR Freight always thrives to build a trusting relationship with its clients, making these insurances available helps achieve the sustainability of each transaction, create a legal settlement in the event of losses, and promote customer value.
- Vehicle services: Provide vehicle service with an exceptional and timely manner. JR Freight’s maintenance procedures are safe, guaranteed, and highly qualified. The service covers maintaining and repairing jobs, ensuring the best trip for clients.
- General civil engineering and construction design, project execution and management: JR Freight provides civil engineering service, majored in planning and constructing client’s transportation infrastructure. The company will be in charge of designing the project, providing support and supervision during the construction process, close inspection is carried out in every step of the project.
- Incidental and related business operation: Support client’s business activities and projects.
Modes of Transportation
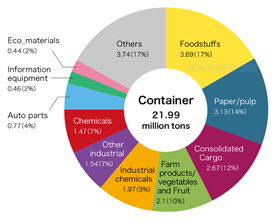
- Container transportation on flatbed trains: Available in road, sea, and air routes with 140 container rail terminals. With the advantage of being the largest railway freight company in Japan and owning a nationwide network of railway, JR Freight’s service offers a flexible process of picking up goods at a different terminal which is the most convenient for customers and delivering to several destinations all over Japan. Containers are able to carry a wide range of products, such as household goods, automobiles, frozen and fresh foods, waste products.
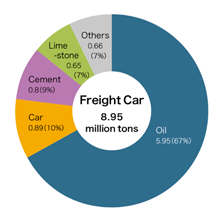
- Freight car for specialized cargo: JR Freight offers specialized freight car with sufficient and high-quality technology to ensure client’s cargoes reach their destination in the original state in the shortest time. Being the oldest freight service company in Japan, JR Freight is committed to contributing to sustainable growth in business and industry of the country; that is why their freight cars offer environmental benefits using energy-efficient engines and technologies. Specialized freight trains are available for bulky, large-volume cargo, such as oil, cement, limestone, chemicals, bulky machinery, and other materials.
Japan Freight Innovations and Technologies
JR Freight uses a wide range of different modes of transportation all via railway. They develop their locomotives, freight trains, and containers using the most advanced technology in accordance with the evolving needs of Japan’s transportation needs. The Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport reports that rail freight is the most eco-friendly mode of freight transportation (JR Freight, 2019).
Below is a chart showing the CO2 emissions per unit volume of transport:
JR Freight six types of railway transportation conceptualized based on the foreseen needs of the future generation. They have the M250 express container train ‘Super Rail Cargo’, EF510 AC/DC electric locomotive, EH200 DC electric locomotive, The ECO-POWER ‘Kintaro’, The ECO-POWER ‘Momotaro’, and the new tank trains. Since JR Freight has been operating in the railway business since 1987, over 30 years, they can easily forecast the future requirements of their clients and know the specific features that would benefit Japanese businesses.
Their transportation systems are reliable and they state on their website the reasons why companies can trust them to deliver on time and risk-free. The Super Liner services all of the major cities in Japan. Their largest container hub in Tokyo offers complete services such as disposal of goods, storage, distribution, and transshipment. Punctuality is attained through following signalled instructions. Using the Effective and Speedy “E&S” container handling system, containers are loaded directly on the tracks which make the process faster.
When it comes to safety and dependability, JR Freight also assures their business partners that the systems they use are always up-to-date that can handle disruptions that are caused by natural disasters. Every minute, they keep an eye on all freight services to check for possible system issues. The chassis and bogies are regularly inspected for issues and they use the latest technology to check the safety of the tracks.
JR Freight also uses data from Driving Support System (PRANETS or Positioning system for RAil NETwork and Safety operating), GPS Information, and Agile Crew and Training Information System for accurate detection of locations of each train with voice guidance providing information of the train’s exact departure time, the train’s speed, and the speed limit. All these technologies make for a reliable, on-time, and safe railway system.
Scenario Analysis
In our scenario,
Shipper: SR Exports, Kelowna, B.C.
Buyer: Wet Works Inc., Osaka, Japan.
Shipping Product: Plumbing Supplies
Product details: 5 skids of 48 in x 40 in x 36 in. Each skid is 385 lb.
The goods are to be shipped from SR Exports to Vancouver Airport, loaded onto a flight to Tokyo by Air Canada Cargo.
From Tokyo Airport, Japan Freight Railway Company will deliver the goods to Osaka.
Then Wet Works Inc. will take over the goods to carry to their warehouse.
The buyer wants the goods to be delivered to Osaka, where he will assume the risk for the goods, account for them to customs, and pay duties and taxes.
Since the risk will be assumed by the buyer in Osaka and he will be paying for the duties and taxes, the Incoterms should be chosen as:
DAP, Wet Works Inc., 1200 Kawasaki Street, Osaka, Incoterms® 2010.
In terms of charges, we have air freight and rail freight charges in our scenario as both shipper and buyer are using their own trucks for land transportation which results in no land freight charge for any party.
Air Freight Charges
Actual Weight: 385 lb x 5 skids = 1,925 lbs
Volume Weight: (48 in x 40 in x 36 in x 5 skids) / 166 = 2,082 lbs
Chargeable Weight: 2,082 lbs
After calculating chargeable weight, we check the Air Canada Cargo’s rates table to find out the applicable rate for our freight.
From/to: Vancouver Airport (YVR)
According to the above table, the rate applied to our freight is 19.20 CAD.
Chargeable Weight: 2,082 lbs
Applicable Rate: 19.20 CAD
Total Charge: 2,082 X 19.20 = 39,974 CAD
Rail Freight Charges
Actual Weight: 385 lb x 5 skids = 1,925 lbs
Volume Weight: (48 in x 40 in x 36 in x 5 skids) / 1,728 = 200 cubic feet x 10 = 2,000 lbs
Chargeable Weight: 2,000 lbs
After calculating chargeable weight, we check the Japan Freight Railway Company’s rates table to find out the applicable rate for our freight.
From/to: Tokyo
According to the above table, the rate applied to our freight is 17.00 CAD.
Chargeable Weight: 2,000 lbs
Applicable Rate: 17.00 CAD
Total Charge: 2,000 x 17.00 = 34,000 CAD
When we sum up the air freight and rail freight charges, the total freight charge is 73,794 CAD.
References
EJRCF. (2001). Rail freight in Japan. Retrieved from http://www.ejrcf.or.jp/jrtr/jrtr26/pdf/f08_iwa.pdf
JR Freight Company. (2019). Environmentally friendly rail transportation. Retrieved from https://www.jrfreight.co.jp/en/ecology
JR Freight Company. (2019). Main Data (in Corporate Data). Retrieved from https://www.jrfreight.co.jp/en/main-data
The World Bank. (2018). Logistics performance index 2018. Retrieved November 29, 2019 from https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/infographic/2018/07/24/logistics-performance-index-2018
Warnock, E. (2018). Lessons from Railway Privatization in Japan. Tokyo Review. Retrieved November 29, 2019 from https://www.tokyoreview.net/2018/10/japan-railway-privatization/