CIFFA Exam Sample Questions and Answers – Commercial Documentation and Regulatory Compliance

CIFFA Exam Sample Questions and Answers – Commercial Documentation and Regulatory Compliance
- Who issues an export permit?
The Export and Import Controls Bureau (EICB) authorizes, under the discretion of the Minister of International Trade (Global Affairs Canada) the import and export of goods restricted by quotas and/or tariffs.
- What is the Area Control List?
The ACL is a list of countries for which export permits are required to export any and all goods.
- Name five items on the Export Control List.
Export controls are in place to regulate such goods as:
Agricultural products: refined sugar, sugar-containing products and peanut butter
Textiles and clothing
Military, strategic dual-use goods
Nuclear energy materials and technology
Missile, chemical or biological goods of non-proliferation concern
Softwood lumber, unprocessed logs and certain other forest products
Miscellaneous goods including goods of U.S.-origin, roe herring and certain items with medical value
All goods destined for countries on the Area Control List.
- Who supplies the blank consular invoice forms, and who certifies them?
The consulate of the destination country.
- Name the parties who can sign a general certificate of origin.
The exporter/shipper.
The forwarder as agent for the shipper/manufacturer.
The manufacturer.
The shipper’s/manufacturer’s legal representative. (The commissioner for taking oaths witnesses the signature and stamps it and the Board of Trade or Chamber of Commerce authenticate it).
- Give the most important reason why a certificate of origin may be required.
To obtain preferred import status for the merchandise and possibly a lower rate of duty.
- Do goods shipped under the NAFTA need a certificate of origin? If so what kind?
Yes, they need a North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) certificate of origin.
- Name three items for which an import permit is required.
- Certain agricultural products
- Certain textiles and clothing
- Certain carbon steels and specialty steels
- Specified endangered species of wild flora and fauna
- Any products thereof
- Certain dairy products
- When moving exhibition goods to two or more different countries, what document would you recommend to make import and export procedures easier?
A.T.A. Carnet.
- A client approaches your company and wants to export a stuffed (taxidermied) bear via air freight to Hong Kong. What must you do prior to proceeding?
Verify if an export permit as well as a CITES permit is required prior to shipment.
- Where would you get information on documentary requirements for a given country?
Your company’s agent at destination, or Migra’s Canadian Export Guide.
- Name two purposes of a commercial invoice.
It is the document against which the buyer (importer) pays the seller (exporter). It is also the document used to provide information to:
The government of the country of export
The government of the country of transit
The government of the country of import.
As the document used by the buyer (importer) that will assist in the clearance of goods at the country of destination, it is also the basis for the Canadian Customs entry and is used to determine duties and taxes so long as it meets certain requirements.
- List items that should be shown on the commercial invoice.
- Importer’s name and address
- Description of the goods, H.S. if possible
- Weight of shipment
- Individual value of pieces along with the number of goods and the total value
- The currency of the transaction
- The terms of payment
- The terms of delivery
- MOST IMPORTANT – the commercial invoice should be dated and signed
- Exporter’s name and address
- What are the three most common errors made on commercial invoices?
Missing currency designation.
Failure signature (although it’s not always required).
Missing date.
- Name two purposes for the packing list.
Identifies the location of goods within a shipment.
In the case of an insurance claim, helps to identify the goods.
- Who issues an import permit in Canada?
Global Affairs Canada
- Above what value for an export shipment must you issue an export declaration (CAED or B13A)?
All shipments leaving Canada with a value above CAN $2,000.00.
Note: A B13A is not required if the final destination of the goods is in the United States of America.
- What is the function of the B13A? Where or with whom is it filed?
To provide governmental agencies with statistical information regarding what goods are being exported to where, when and to whom. The document is filed with Canada Customs and remains in Canada.
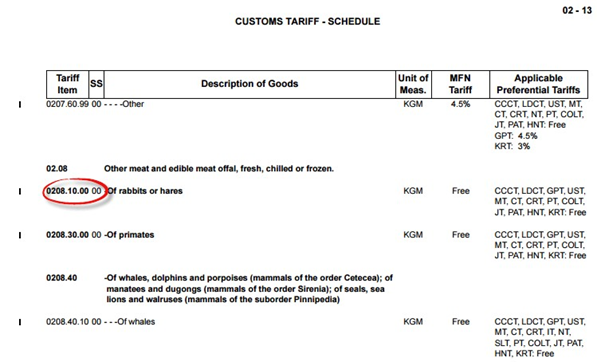
- What is the HS code? Give the full name.
The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS) (example below) forms the basis of the Customs Tariff. The HS was developed and is maintained by the WCO and it is the standard coding structure and related product descriptions used in international trade to determine appropriate duty rates, negotiate trade agreements, maintain trade statistics and identify goods and shipments that pose risk to the health, safety and security in Canada.
- Can you apply for an export permit if the exporter is not residing in Canada but the goods are of Canadian origin and exported through a Canadian port?
Yes, but then the agent acting on behalf of the exporter becomes responsible for any offences committed respecting the permit.
- What international convention regulates the traffic of endangered species?
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, referred to as CITES.
- What is CRF?
Clean Report of Findings. An inspection certificate, issued by an inspector, required by certain countries to allow importation. The inspection is done prior to the export of the goods.





